What is Brain Tumor?

A brain tumor is excess growth of abnormal tissues in your brain. There are many
different causes of a brain tumor that exist. Many brain tumors are cancerous and many of
them are noncancerous. The beginning stage of a brain tumor is a primary brain tumor and if
cancer starts to develop in the body and spreads to your brain is considered a secondary
brain tumor..
How it can affect the function of the nervous system completely depends upon the exact
location and the growth rate of a brain tumor. The treatment of brain tumor all depend upon
the brain tumor's type, size, and location.
Types of Brain Tumor?
There are about 120 distinct forms of brain tumors, lesions, and cysts, which are distinguished
by where they occur and the sort of cells they include. Certain tumors are often benign
(noncancerous), while others are typically malignant (cancerous). Others have a 50/50 risk of
developing cancer.
Some of the tumors described below are primary tumors:-
Meningioma
Meningioma is a popular primary brain tumor, which results in almost 30% of all brain tumors.
This brain tumor occurs in the meninges, which are the three outer layers of the human body that
help in covering and surrounding the brain under the skull. There is more chance of women in
comparison to males having meningiomas. Meningiomas are noncancerous, slow-growing tumors that
account for around 85 percent of all cases.
Pituitary Adenoma
The most frequent kind of pituitary tumor is an adenoma, which is a tumor that develops in the
gland tissues. Pituitary adenomas arise from the pituitary gland and grow slowly. Adenomas
account for around 10% of all primary brain tumors. They have the potential to induce eyesight
and endocrinological issues.
Craniopharyngioma
These benign tumors can look like solid tumors or cysts and develop around the pituitary gland.
Craniopharyngiomas frequently push on nerves, blood vessels, or brain tissue around the
pituitary gland. They, like adenomas, can cause eyesight and endocrinological problems. They
typically affect toddlers, teenagers, and people over the age of 50.
Schwannoma
Acoustic neuromas (vestibular schwannomas) are slow-growing, benign tumors of the nerve that
links the ear to the brain. Acoustic neuromas account for less than 8% of all primary brain
tumors. They often appear in middle-aged individuals, grow on the nerve sheath (the coating that
surrounds the nerve fibers), and frequently cause hearing loss. Schwannomas can potentially
cause damage to the trigeminal nerve. These are known as trigeminal schwannomas, and they can
cause facial pain.
Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma
Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma, also known as juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma, is a benign
skull base tumor in the nose that is most commonly found in teen boys. It is the most frequent
benign nasopharyngeal tumor which is in the backspace of the nose. It spreads to the nose and
causes symptoms such as congestion and nosebleeds.
Choroid Plexus Tumor
Choroid plexus tumors are uncommon tumors that develop in the choroid plexus, the region of the
brain that creates cerebrospinal fluid within its ventricles. Approximately 90% of these tumors
are benign. They are most common in children under the age of two and can lead to hydrocephalus,
or an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, as they develop. Choroid plexus carcinoma is a rare
malignant kind of choroid plexus tumor.
Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor
This is a neuronal-glial brain tumor, which means it is made up of both neurons and supporting
cells. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors are uncommon benign tumors that develop in the
tissues that surround the brain and spinal cord. These tumors, which are most commonly detected
in adolescents and teenagers, can induce seizures. Gangliogliomas, gangliocytomas, and
rosette-forming tumors are examples of neuronal-glial brain cancers.
Neurofibroma
Neurofibromas are painless, benign tumors that can form on nerves anywhere in the body. These
soft, fleshy growths can form in the brain, on cranial nerves, or the spinal cord in some
situations.
Symptoms of Brain Tumor
The following symptoms of Brain Tumor or indicators may be experienced by those who have a brain
tumor. A symptom, such as tiredness, nausea, or discomfort, is something that only the person
experiencing it can recognize and explain. Brain tumor symptoms might be generic or specialized.
The pressure of the tumor on the brain or spinal cord causes a general symptom. Certain symptoms
occur when a specific area of the brain is not functioning properly due to the tumor. Many
persons with brain tumors were detected after going to the doctor with a symptom, such as a
headache or other abnormalities.
Some of the general signs and symptoms caused due to brain tumors are:-
- You may feel the change in patterns of headaches
- Your headache gradually become common or severe
- You may feel like discomfort or vomiting
- You may have visionary problems like blurred vision,
double vision, or loss of peripheral vision.
- You may lose slowly- slowly sensation or movement in
an arm or a leg
- You may feel confusion in daily activities
- You may have a problem while speaking
- You may have a problem balancing
- You may feel tired very soon
- You may feel difficulty in making decisions
- You may have difficulty in following simple commands
- You may feel changes in your behavior and personality
- You may have difficulty in hearing
If you are experiencing these symptoms, consult with the best neurologist in Jaipur.
Diagnosis of a Brain Tumor
If it is found that you are suffering from a brain tumor then your doctor will recommend you
some tests and procedures including:

A neurological exam may entail testing your vision, hearing,
balance, coordination, strength, and reflexes, among other things.
Difficulty in one or more regions may reveal information about the section
of your brain that is likely to be impacted by a brain tumor.
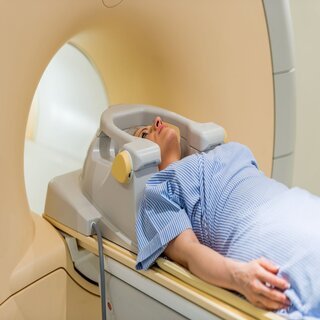
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is frequently used to aid in
the diagnosis of brain malignancies. During your MRI examination, a dye may
be injected into a vein in your arm. A variety of specialist MRI scan
components, including functional MRI, perfusion MRI, and magnetic resonance
spectroscopy, may aid your doctor in assessing the tumor and planning
therapy.

A Biopsy can be done as part of a surgery to remove the brain
tumor, or it can be done with a needle. A stereotactic needle biopsy may be
performed for brain tumors in difficult-to-reach places or in extremely
sensitive sections of your brain that might be injured by a more thorough
procedure.
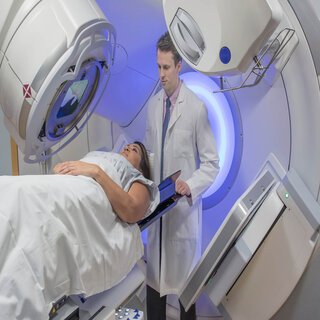
To destroy tumor cells, radiation treatment employs high-energy
beams such as X-rays or protons. Radiation therapy can be delivered by a
machine outside your body (external beam radiation) or, in rare cases,
radiation can be delivered within your body near your brain tumor
(brachytherapy).
Radiation therapy has traditionally used X-rays, but a newer kind of this
treatment employs proton beams.
Why is Dr.Sumit Kamble suitable for Brain Tumour Treatment in Jaipur?
Dr Sumit Kamble is a senior consultant neurologist at CKS Hospitals and when it comes to
brain tumour treatment. He is considered as the best neurologist in Jaipur who has
specialized in treating ailments such as brain
stroke treatment, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and spine difficulties. Dr Sumit
Kamble has over ten years of expertise in his area.
He has done his MBBS from Govt Medical College, Nagpur, MD in General Medicine from Govt
Medical College, Baroda, and DM in Neurology from Govt Medical College, Kota. Dr.Sumit
Kamble has also done Fellowship in Pain Management (FIPM) from DPMC, Delhi. He is an active
life member of the prestigious American Society of Neurology and the Indian society of
Neurology. He has done Fellowship in Neurology from PGI Chandigarh.
Frequently Asked Question about Brain Tumor
Brain tumours are more commonly seen in the nervous system. It can arise as
a result of a variety of factors and events. A brain tumour is a mass of
tissue that develops in the brain as a result of abnormal cell growth. It
spreads as a result of increased cell proliferation and cessation of normal
function.
Brain tumours can be difficult to identify, thus it is critical for the
patient to speak with a neurosurgeon who specializes in this field. It is a
form of tumour that begins in the brain, most commonly in the cerebrum or
cerebellum. And it is diagnosed by determining if any abnormal tissue can be
detected using imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, ultrasounds, and so on.
The most prevalent malignant tumour in humans is brain cancer. It is
critical to begin treatment as soon as possible. Brain tumour therapy varies
based on the location and size of the tumour, although there are some common
principles for its management. Doctors frequently.




